 The SAS® platform is now open to be accessed from open-source clients such as Python, Lua, Java, the R language, and REST APIs to leverage the capabilities of SAS® Viya® products and solutions. You can analyze your data in a cloud-enabled environment that handles large amounts of data in a variety of different formats. To find out more about SAS Viya, see the “SAS Viya: What's in it for me? The user.” article.
The SAS® platform is now open to be accessed from open-source clients such as Python, Lua, Java, the R language, and REST APIs to leverage the capabilities of SAS® Viya® products and solutions. You can analyze your data in a cloud-enabled environment that handles large amounts of data in a variety of different formats. To find out more about SAS Viya, see the “SAS Viya: What's in it for me? The user.” article.
This blog post focuses on the openness of SAS® 9.4 and discusses features such as the SASPy package and the SAS kernel for Jupyter Notebook and more as clients to SAS. Note: This blog post is relevant for all maintenance releases of SAS 9.4.
SASPy
The SASPy package enables you to connect to and run your analysis from SAS 9.4 using the object-oriented methods and objects from the Python language as well as the Python magic methods. SASPy translates the objects and methods added into the SAS code before executing the code. To use SASPy, you must have SAS 9.4 and Python 3.x or later.
Note: SASPy is an open-source project that encourages your contributions.
Note: SASPy is an open-source project that encourages your contributions.
After you have completed the installation and configuration of SASPy, you can import the SASPy package as demonstrated below:
Note: I used Jupyter Notebook to run the examples in this blog post.
Note: I used Jupyter Notebook to run the examples in this blog post.
1. Import the SASPy package:

2. Start a new session. The sas object is created as a result of starting a SAS session using a locally installed version of SAS under Microsoft Windows. After this session is successfully established, the following note is generated:

Adding Data
Now that the SAS session is started, you need to add some data to analyze. This example uses SASPy to read a CSV file that provides census data based on the ZIP Codes in Los Angeles County and create a SASdata object named tabl:
 To view the attributes of this SASdata object named tabl, use the PRINT() function below, which shows the libref and the SAS data set name. It shows the results as Pandas, which is the default result output for tables.
To view the attributes of this SASdata object named tabl, use the PRINT() function below, which shows the libref and the SAS data set name. It shows the results as Pandas, which is the default result output for tables.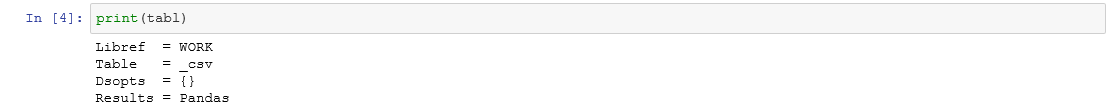
How to code in Python with SAS 9.4
2 The SAS® platform is now open to be accessed from open-source clients such as Python, Lua, Java, the R language, and REST APIs to leverage the capabilities of SAS® Viya® products and solutions. You can analyze your data in a cloud-enabled environment that handles large amounts of data in a variety of different formats. To find out more about SAS Viya, see the “SAS Viya: What's in it for me? The user.” article.
The SAS® platform is now open to be accessed from open-source clients such as Python, Lua, Java, the R language, and REST APIs to leverage the capabilities of SAS® Viya® products and solutions. You can analyze your data in a cloud-enabled environment that handles large amounts of data in a variety of different formats. To find out more about SAS Viya, see the “SAS Viya: What's in it for me? The user.” article.
This blog post focuses on the openness of SAS® 9.4 and discusses features such as the SASPy package and the SAS kernel for Jupyter Notebook and more as clients to SAS. Note: This blog post is relevant for all maintenance releases of SAS 9.4.
SASPy
The SASPy package enables you to connect to and run your analysis from SAS 9.4 using the object-oriented methods and objects from the Python language as well as the Python magic methods. SASPy translates the objects and methods added into the SAS code before executing the code. To use SASPy, you must have SAS 9.4 and Python 3.x or later.
Note: SASPy is an open-source project that encourages your contributions.
Note: SASPy is an open-source project that encourages your contributions.
After you have completed the installation and configuration of SASPy, you can import the SASPy package as demonstrated below:
Note: I used Jupyter Notebook to run the examples in this blog post.
Note: I used Jupyter Notebook to run the examples in this blog post.
1. Import the SASPy package:
2. Start a new session. The sas object is created as a result of starting a SAS session using a locally installed version of SAS under Microsoft Windows. After this session is successfully established, the following note is generated:

Adding Data
Now that the SAS session is started, you need to add some data to analyze. This example uses SASPy to read a CSV file that provides census data based on the ZIP Codes in Los Angeles County and create a SASdata object named tabl:

To view the attributes of this SASdata object named tabl, use the PRINT() function below, which shows the libref and the SAS data set name. It shows the results as Pandas, which is the default result output for tables.

Using Methods to Display and Analyze Data
This section provides some examples of how to use different methods to interact with SAS data via SASPy.
Head() Method
After loading the data, you can look at the first few records of the ZIP Code data, which is easy using the familiar head() method in Python. This example uses the head() method on the SASdata object tabl to display the first five records. The output is shown below:
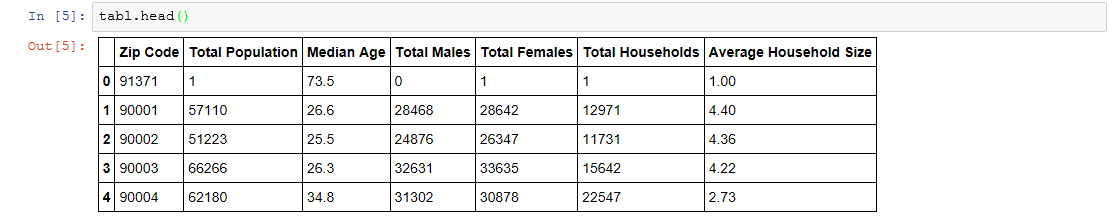
Describe() Method
After verifying that the data is what you expected, you can now analyze the data. To generate a simple summary of the data, use the Python describe() method in conjunction with the index [1:3]. This combination generates a summary of all the numeric fields within the table and displays only the second and third records. The subscript works only when the result is set to Pandas and does not work if set to HTML or Text, which are also valid options.
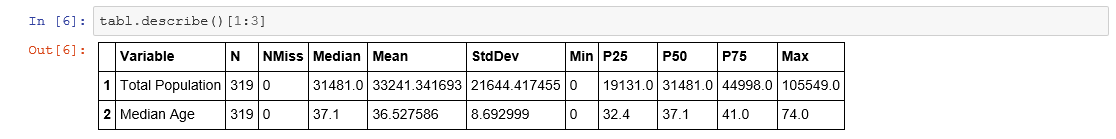
Teach_me_SAS() Method
The SAS code generated from the object-oriented Python syntax can also be displayed using SASPy with the teach_me_SAS() method. When you set the argument in this method to True, which is done using a Boolean value, the SAS code is displayed without executing the code:

ColumnInfo() Method
In the next cell, use the columnInfo() method to display the information about each variable in the SAS data set. Note: The SAS code is generated as a result of adding the teach_me_SAS() method in the last section:

Submit() Method
Then, use the submit() method to execute the PROC CONTENTS that are displayed in the cell above directly from Python. The submit method returns a dictionary with two keys, LST and LOG. The LST key contains the results and the LOG key returns the SAS log. The results are displayed as HTML. The HTML package is imported to display the results.

The SAS Kernel Using Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook can run programs in various programming languages including SAS when you install and configure the SAS kernel. Using the SAS kernel is another way to run SAS interactively using a web-based program, which also enables you to save the analysis in a notebook. See the links above for details about installation and configuration of the SAS kernel. To verify that the SAS kernel installed successfully, you can run the following code: jupyter kernelspec list

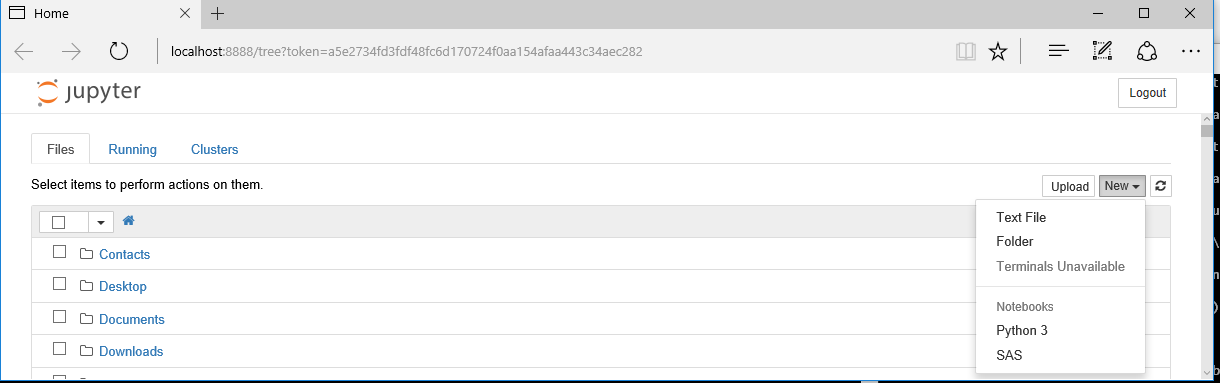
From the command line, use the following command to start the Jupyter Notebook: Jupyter notebook. The screenshot below shows the Jupyter Notebook session that starts when you run the code. To execute SAS syntax from Jupyter Notebook, select SAS from the New drop-down list as shown below:
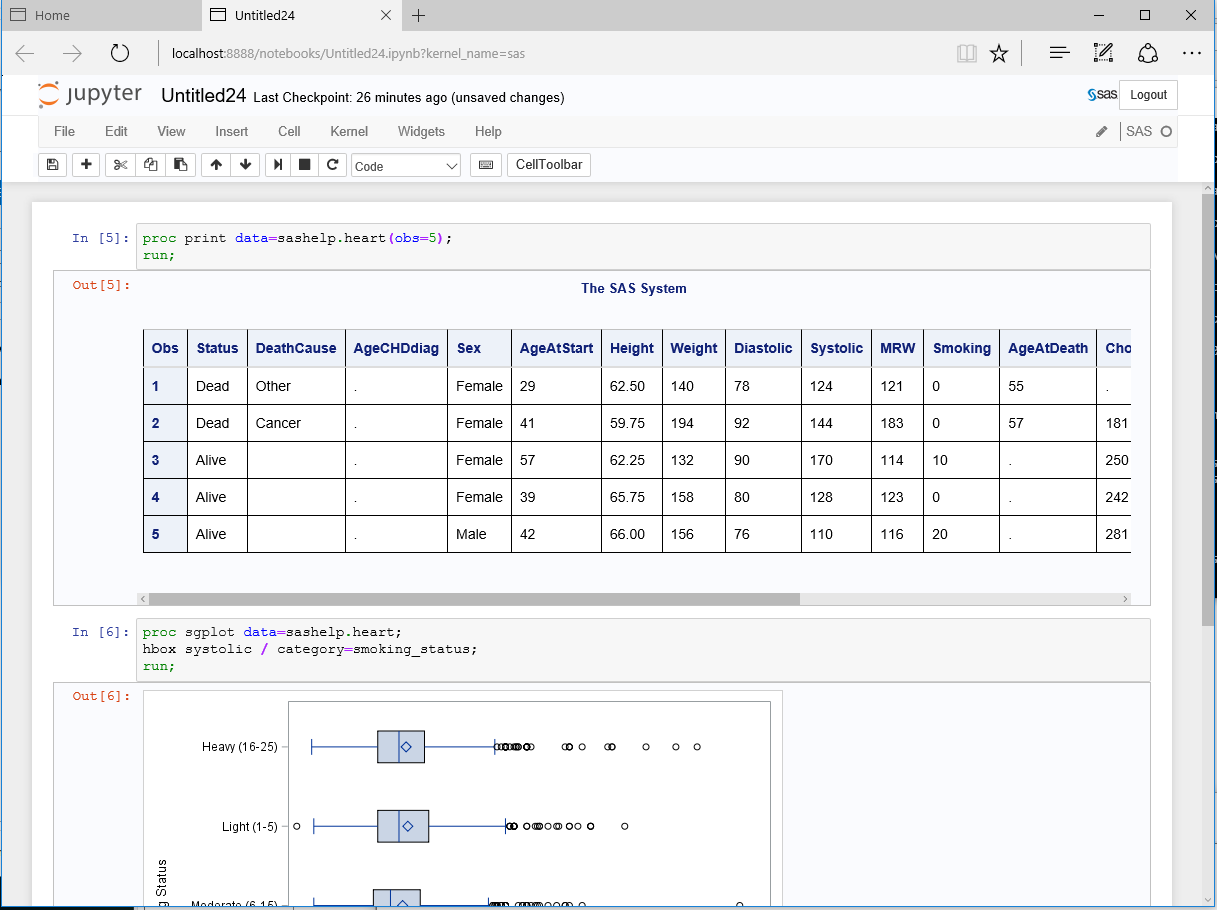
You can add SAS code to a cell in Jupyter Notebook and execute it. The following code adds a PRINT procedure and a SGPLOT procedure. The output is in HTML5 by default. However, you can specify a different output format if needed.

You can also use magics in the cell such as the %%python magic even though you are using the SAS kernel. You can do this for any kernel that you have installed.

Other SAS Goodness
There are more ways of interacting with other languages with SAS as well. For example, you can use the Groovy procedure to run Groovy statements on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). You can also use the LUA procedure to run LUA code from SAS along with the ability to call most SAS functions from Lua. For more information, see “Using Lua within your SAS programs.” Another very powerful feature is the DATA step JavaObject, which provides the ability to instantiate Java classes and access fields and methods. The DATA step JavaObject has been available since SAS® 9.2.
Resources
Introducing SASPy: Use Python code to access SAS
Source By: https://blogs.sas.com/content/sgf/2018/01/10/come-on-in-were-open-the-openness-of-sas-94/
Source By: https://blogs.sas.com/content/sgf/2018/01/10/come-on-in-were-open-the-openness-of-sas-94/
Authorized SAS TRAINING | SAS CERTIFICATION | SOFTWARE PURCHASE | BUSINESS CONSULTING | TECHNICAL SUPPORT ON SAS || SAS STAFFING SOLUTION
SAS
Training & Placement Programs with Internship: Epoch Research
Institute India Largest and Oldest #SASTraining Institute (#epochsastraining)
https://twitter.com/epochresearch https://www.facebook.com/EpochResearchInstitute/ http://www.epochresearchinstitute.com/ https://www.linkedin.com/in/epochresearch/ https://www.youtube.com/user/epochresearch07/
Mail Us: info@epoch.co.in
We are Located:
Ahmedabad : B-603,Shapath 4 S.G.Highway Ahmedabad, Gujarat 380058
Bangalore : 1st Floor Innovation, No 101, Amarjyothi, Basaveshwara HBCS Layout, Domlur, Layout, Domlur, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560071
#EpochSASAcademyClinicalProgramming #EpochClinicalSASProgramming #epochsasclinicalauthorisedtraining
#epochClinicalSASonlineTraining
#ClinicalSASTraininginBangalore #ClinicalSASTraininginIndia
#ClinicalSASTrainingingujarat #ClinicalSASTraininginJobs
#ClinicalSASTraininginPlacement #ClinicalSASjobs
#epochSASAcademyforClinicalProgramming
#epochSASClinicalProgrammingFundamentals
#epochAppliedClinicalDataAnalysisandReporting #epochsasbesttrainingindia
#epochsasreport #epochsasgraph #epochcdiscstdmsas #cdisc #stdm
#epochsasclinicaldatamangement #epochsasBiostatistics
#epochsasfresherjobsclinical #clinicalresearchtraining
#epochsasclinicaltrialprogrammer #epochsasglobalcertification
#epochbasesas #epochadvancesas

It is very use full blog and very important information about SAS.
ReplyDeleteOnline SAS Training
SAS training
Really great information you provided here.
ReplyDeleteAlso check the best institute for Medial Research and Training
Clinosol - Medical Research & Training
https://clinosol.com/
SAS is an open - source software, and features like the SASPy package for Jupyter Notebook and the SAS kernel for Jupyter are discussed in this blog article. NIce article.
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteIt provides such amazing information the post is really helpful and very much thanks to you Best SAS institute in india